Medicina, Free Full-Text
5 (549) In stock
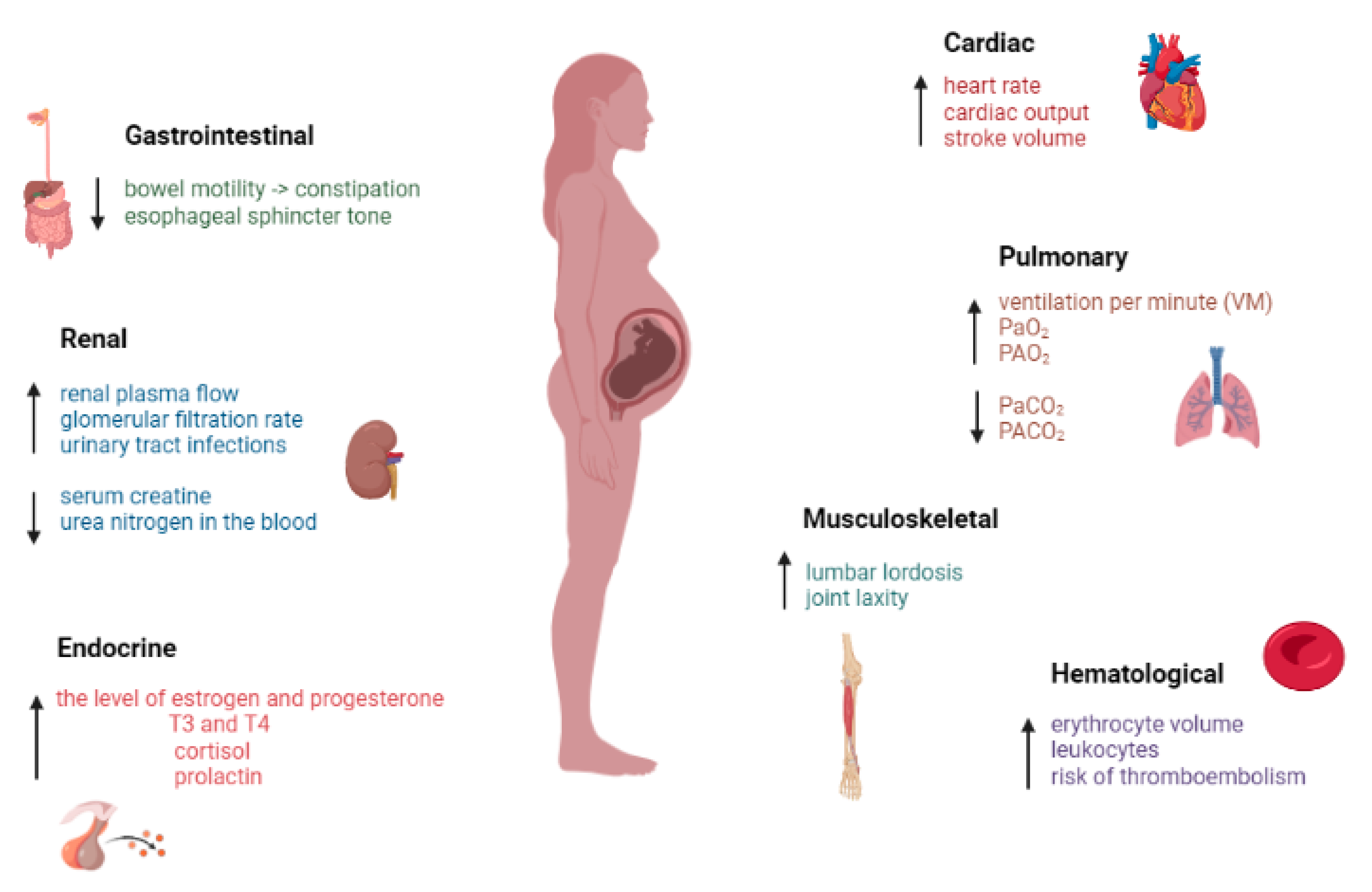
Background and Objectives: During pregnancy, women undergo various physiological and anatomical changes that are accentuated as the pregnancy progresses, but return to their previous state a few weeks/months after the pregnancy. However, a targeted therapeutic approach is needed. Most of the time, during this period, these changes precipitate the appearance of pain, musculoskeletal pain being the most common. Pregnant women should avoid treating musculoskeletal pain with medication and should choose alternative and complementary methods. Exercise along with rest is the basis for treating chronic musculoskeletal pain. Side effects of physical therapy are rare and, in addition, it is not contraindicated in pregnant women. The benefits of this type of treatment in combating pain far outweigh the risks, being an easy way to improve quality of life. The objective of this article is to discuss the management of musculoskeletal pain during pregnancy, to identify the main musculoskeletal pain encountered in pregnant women along with drug treatment, and to expose the beneficial effects of alternative and complementary methods in combating pain. Materials and Methods: A literature search was conducted using medical databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect, using the keywords “changes of pregnancy”, “musculoskeletal pain”, “pregnancy pain”, “pain management”, “pharmacological approach”, “alternative and complementary treatment” and specific sites. Information was collected from studies whose target population included pregnant women who complained of musculoskeletal pain during the 9 months of pregnancy; pregnant women with other pathologies that could increase their pain were not included in this review. Results: The articles related to the most common non-obstetric musculoskeletal pain in pregnancy along with pharmacological treatment options and alternative and complementary methods for musculoskeletal pain management during pregnancy were selected. Conclusions: The results were used to guide information towards the safest methods of therapy but also to raise awareness of the treatment criteria in order to compare the effectiveness of existing methods. Treatment must consider the implications for the mother and fetus, optimizing non-pharmacological therapeutic options.

Are you looking for a FREE resource for daily quizzes on all topics related to medicine and surgery?!? We also have 100s of cheat sheets

Stethoscope On Book Stock Photo - Download Image Now - Healthcare And Medicine, Medical Exam, Studying - iStock
Medicina, Free Full-Text, Medical Patch

Medicina, Free Full-Text

Free and customizable medicine templates

Need your help: A master list of free EM and Critical Care blog and podcast sites

FreeGreens™ - Natural Medicine Formulas
Medicina, Free Full-Text
Oxidative stress. From normal cells, to oxidative stress and
The features and aetiology of Fournier's gangrene. - Abstract

Massachusetts Medical Society: Sample Articles from Vital Signs
PDF) Acute urinary retention in pregnancy: A case presentation and review of the literature
Acute urinary retention - WikEM
URINARY INCONTINENCE AND URINARY RETENTION. Urinary incontinence (UI) - ppt download
Uterine Incarceration: Rare Cause of Urinary Retention in Healthy
 Pilates solo ou em aparelhos: diferenças e qual escolher - Minha Vida
Pilates solo ou em aparelhos: diferenças e qual escolher - Minha Vida Liforme Blossoming Lotus Yoga Mat - Purple
Liforme Blossoming Lotus Yoga Mat - Purple- Champion Motion Control Underwire High Impact Sports Bra B1526, Up
 4 Styles Women's Dragon Vest Print Sleeveless Tank Top And
4 Styles Women's Dragon Vest Print Sleeveless Tank Top And Sharemen Pants for Women Comfy Summer Casual Cotton Linen Wide Leg Drawstring High Waist Loose Palazzo Pants Trousers Pants – Yaxa Colombia
Sharemen Pants for Women Comfy Summer Casual Cotton Linen Wide Leg Drawstring High Waist Loose Palazzo Pants Trousers Pants – Yaxa Colombia Ralph Lauren vs Polo: The Striking Difference No One Talks About
Ralph Lauren vs Polo: The Striking Difference No One Talks About
